3-文件流
本文共 3261 字,大约阅读时间需要 10 分钟。
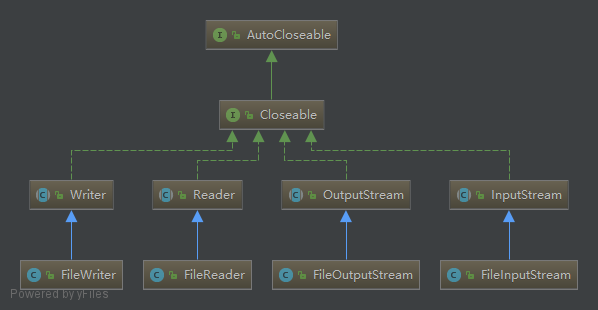
文件流是我们接触最多的一种io流,主要是对文件的一种数据读写操作。
主要有以下几种:
针对,最上层四种,下面有demo进行相关操作:
关键点:
1、四种file io流,都有两种构造函数:construct(String fileName)/construct(File file)
2、四种file io流,都实现了AutoCloseable接口,jdk1.7采用try-with-resources管理AutoCloseable对象,会自动帮我们关闭,省去了,finally关闭语句块。
3、输入流的物理节点如果不存在,需要显式创建,否则会抛异常,输出流的物理节点不存在,不需要显式创建,会自动帮我们创建
package com.wlt;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.*;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;/** * 复习File相关的io流 * @author 魏霖涛 * @since 2018/2/24 0024 */public class ReviewFileIO { @Test public void fileinputstream() throws IOException{ try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("./pom.xml")){ byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int hasRead = 0; while ((hasRead = fileInputStream.read(buf)) > 0) { System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, hasRead)); }// while ((hasRead = fileInputStream.read(buf)) > 0) {// //将字节强制转换成字符后逐个输出,能实现和上面一样的效果。但是如果源文件是中文的话可能会乱码// for (byte b : buf) {// char ch = (char) b;// if (ch != '\r') {// System.out.print(ch);// }// }// } } } @Test public void filereader() throws IOException{ try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("./pom.xml")){ char[] chars = new char[32]; int hasRead = 0; // 每个char都占两个字节,每个字符或者汉字都是占2个字节,因此无论buf长度为多少,总是能读取中文字符长度的整数倍,不会乱码 while ((hasRead = fileReader.read(chars)) > 0) { System.out.print(new String(chars, 0, hasRead)); } //效果和上面一样// while ((hasRead = fileReader.read(chars)) > 0) {// for (char ch : chars) {// if (ch != '\r') {// System.out.print(ch);// }// }// } } } @Test public void fileoutputstream() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { File file = new File("fileoutputsream.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } else { //默认写文件是覆盖的// file.delete();// file.createNewFile(); } try ( //在try()中打开文件会在结尾自动关闭 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("pom.xml"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); ) { byte[] buf = new byte[4]; int hasRead = 0; byte[] tmp = (""+new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())+"\n").getBytes(); fos.write(tmp); while ((hasRead = fis.read(buf)) > 0) { //每读取一次就写一次,读多少就写多少 fos.write(buf, 0, hasRead); } System.out.println("write success"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Test public void filewriter() throws IOException { File file = new File("filewriter.txt"); if (!file.exists()) { file.createNewFile(); } try (FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file)) { fw.write("天王盖地虎\r\n"); fw.write("宝塔镇河妖\r\n"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}参考:
你可能感兴趣的文章